Nasal polyps also called “Nasal polyposis” are painless and benign (noncancerous) growths. They form in the mucosa (thin, soft tissue) that lines our nasal and sinus passages. They usually appear on both sides of our nose. Nasal polyps can get irritated and swollen, making it hard for patient to breathe through nose. They happen most often in people with asthma, allergies, repeat infections or nasal inflammations.
Small polyps are teardrop shaped. But as they grow larger, they often resemble peeled grapes that are pink, yellow or gray.
Nasal polyps affect up to 40% of the general population. Anyone can get them. But they’re twice as common in men.
Symptoms and Causes
Nasal polyp symptoms
Small polyps in our nose might not cause symptoms at all. But if they start to grow, one could develop:
- Nasal congestion,
- Rhinorrhea,
- Headaches,
- Loss of taste and smell,
- Nosebleeds,
- Postnasal drip,
- Sinus pressure,
- Snoring.
When polyps grow large enough, they can block our nasal passages and sinuses, leading to:
- Frequent asthma attacks (in people with asthma).
- Sinusitis (repeated sinus infections).
- Sleep apnea or other sleep disorders.
- Difficulty breathing, even if patient don’t have asthma.
Nasal polyps are soft, painless, noncancerous growths that can form in the lining of our nose or sinuses.
Nasal polyp causes
Inflammation causes nasal polyps; but some people develop polyps because of chronic inflammation along with chronic veins congestions for example patients with varicose veins or deep vein thrombosis.
Chronic sinusitis — from allergies, infection or asthma — seems to be the most common reason polyps appear. Chronic sinusitis refers to nasal and sinus inflammation that’s lasted three months or longer. But several risk factors could contribute to the development of nasal polyps.
appear. Chronic sinusitis refers to nasal and sinus inflammation that’s lasted three months or longer. But several risk factors could contribute to the development of nasal polyps.
Risk factors
A risk factor is something that increases the chance of getting a certain condition. Nasal polyp risk factors include existing health conditions like:
- Asthma,
- Allergic rhinitis (hay fever),
- Chronic sinus infections,
- Cystic fibrosis,
- Hypersensitivity to certain allopathic drugs like NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) etc.
According to allopathic scientists, genetics may also play a role in the development of nasal polyps, for instance, certain gene mutations (changes) may impact how your nasal tissues react to inflammation.
According to Homeopathic scientists, some kinds of mineral deficiencies cause body especially respiratory tract to react on dust, smell, smoke, repeating diseases etc which causes inflammations and chronic inflammations and play an important role in developing polys.
Complications of nasal polyps
Ongoing sinus infections associated with nasal polyps can result in rare but serious complications like:
- Bone infection (osteomyelitis) and bone loss.
- Abscesses (pockets of infection) that can spread to your eye sockets and brain.
- Meningitis (infection of the tissues around your brain and spinal cord).
Diagnosis and Tests
How doctors diagnose nasal polyps
To diagnose nasal polyps, start with a physical examination. During physical examination, a doctor may:
- Look inside patient’s nose with a scope with a camera and light.
- Review patient’s medical history (with a focus on allergies, asthma or sinus infections).
- How long patients have had polyps.
Tests used to diagnose nasal polyps
If your healthcare provider needs more information, they may order one of these imaging tests to help them determine the size and location of each polyp:
- CT (computed tomography) scan.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging).
Also recommend allergy testes. This can help identify allergens that lead to nasal inflammation and polyps.
Allopathic treatment
How are nasal polyps treated?
Nasal polyp allopathic treatment depends on the severity of patient’s condition. Medication and surgery are the two main approaches. 
Even with surgical removal, nasal polyps may grow back over time. A doctor will say to his/her patient about the likelihood of recurrence (return).
Allopathic medication
Allopathic medication doesn’t get rid of nasal polyps; they can just ease symptoms. Common treatments include:
- Steroid nasal sprays to shrink polyps and improve symptoms.
- Oral steroids for example prednisone.
- Biologic medications, such as dupilumab injections. (Dupilumab contains monoclonal antibodies that stimulates immune system and sometimes shrink nasal polyps.
An allopath also may prescribe antibiotics if patient have an infection.
Surgery for nasal polyps
If allopathic medication doesn’t work (in 99% cases) — or if patient have large polyps — patient may need sinus surgery to remove them. An endoscopy is one of minimally invasive procedures:
- Polypectomy. A doctor may use instruments (like surgical scissors or snares) to remove the polyps, or a surgical snare wraps around a polyp.
- Balloon sinuplasty. A surgeon threads a small balloon through patient’s nostril and into sinus cavity. They slowly inflate the balloon to unblock patient’s nasal passages. In some cases, they’ll remove nasal polyps at the same time.
- Functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS). A surgeon uses small instruments to remove polyps, diseased tissue, damaged bone and anything else that obstructs patient’s nasal passages.
Homeopathic treatment for polyps
How are nasal polyps treated without surgery?
In Homeopathy there are many proven medicines for polyps, some of those are:
Acid Nitricum
Selects for its special seat of action the outlets of the body where the mucous membrane and skin meet. Blisters and ulcers in mouth, tongue, nasal passages, genitals; bleed easily. Fissures. Chronic diseases and take cold easily. 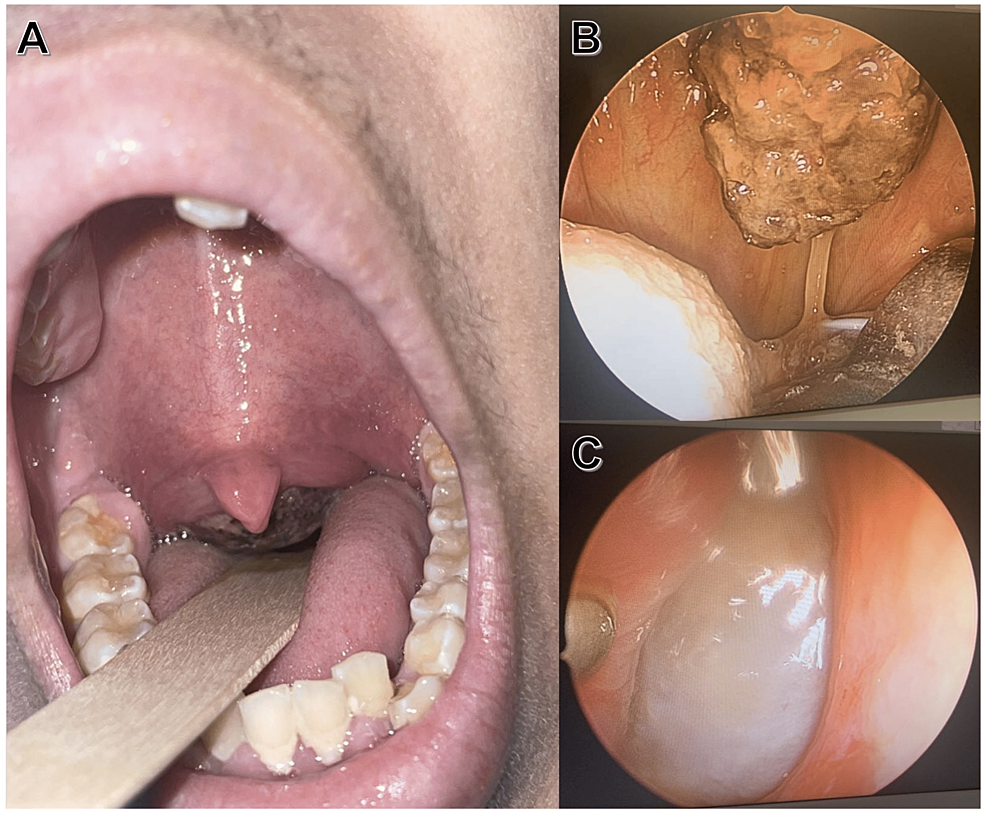
Difficult hearing. Cracking in ears when chewing. Warts, large jagged; bleed on washing. Ulcers bleed easily. Black pores on face, papules. Ozaena. Green casts from nose. Coryza, with sore and bleeding nostrils. Tip red. Stitches in nose as of a splinter. Caries of mastoid. Nosebleed, with chest affections. Chronic nasal catarrh, with yellow, offensive, corrosive discharge. Nasal diphtheria. Putrid breath. Painful pimples on the sides of the tongue. Ulcers in soft palate, with sharp, splinter-like pains. White patches and sharp points, as from splinters, on swallowing.
Phosphorus
Irritated, inflamed and degenerated mucous membranes. Irritated and inflamed serous membranes. Inflamed spinal cord and nerves, causing paralysis. Destroyed bones, especially the nose, lower jaw and tibia. Destructive metabolism.
Hearing difficult, especially to human voice. Re-echoing of sounds. Scurvy. Fungous hematodes and excrescences. Over-sensitive smell. Periostitis of nasal bones. Foul imaginary odors. Chronic catarrh. Polypi; bleeding easily.
Silicea Tera
Imperfect assimilation and consequent defective nutrition. Diseases of bones, caries and necrosis. Silica can stimulate the organism to re-absorb fibrotic conditions (polyps etc) and scar-tissue.
Itching at point of nose. Dry, hard crusts, nasal bones sensitive. Sneezing in morning. Obstructed and loss of smell. Perforation of septum. Felons, abscesses, boils, old fistulous ulcers. Promotes expulsion of foreign bodies and mases from tissues. Crippled nails. Indurated tumors. Abscesses of joints. Side effects of vaccination. Bursa. Lepra, nodes, and coppery spots. Keloid growths. Parotid glands swollen. Hard, cold swelling of cervical glands.
Thuja occidentalis
Acts on skin, blood, gastro-intestinal tract, kidneys, and brain. Pathological vegetations condylomas, warty excrescences, spongy tumors. Moist mucous tubercles. Bleeding fungus growths. Papilloma. Chronic laryngitis. Ranula; varicose veins on tongue, nose and mouth. Pyorrhea alveolaris. Polypi, tubercles, warts epithelioma, naevi, carbuncles; ulcers. Zona; herpetic eruptions. Tearing pains in glands. Glandular enlargement. Nails crippled; brittle and soft. Chronic catarrh; thick, green mucus; blood and pus. On blowing nose, pain in teeth. Ulceration within the nostrils. Dryness of nasal cavities. Painful pressure at root. 
Sangvineria Canadensis
Flushed. Neuralgia: pain extends in all directions from upper jaw. Redness and burning of cheeks. Hectic flush. Fullness and tenderness behind angle of jaws. Edema of larynx. Trachea sore. Hay-fever. Ozaena, with profuse, offensive yellowish discharges. Nasal polypi. Coryza, followed by diarrhea. Chronic rhinitis: membrane dry and congested.
Burning in ears. Earache with headache. Humming and roaring. Aural polypus. Throat swollen, dry and constricted. Ulceration of mouth and fauces, with dry, burning sensation Tongue white; feels scalded. Tonsillitis.
Sanguinarinum Nitricum
Is of use in polypus of the nose. Acute and chronic catarrh. Acute pharyngitis. Smarting and burning in throat and chest. Influenza. Lachrymation, pains in eyes and head, sore scalp; sense of obstruction. chronic follicular pharyngitis.
Nose feels obstructed. Profuse, watery mucus, with burning pain. Enlarged turbinate at beginning of hypertrophic process. Secretion scant, tendency to dryness. Small crusts which bleed when removed. Post-nasal secretions adherent to nasopharynx, dislodged with difficulty. Dry and burning nostrils; watery mucus, with pressure over root of nose. Nostrils plugged with thick, yellow, bloody mucus. Sneezing. Rawness and soreness in posterior nares.
Throat: Rough, dry, constricted, burning. Right tonsil sore, swallowing difficult. Ulceration on the side of the tongue.
Arum Triphyllum
Arum maculatum, Italicum, Dracontium, have the same action as the Triphyllum. Soreness of nostrils. Acrid, excoriating discharge, producing raw sores. Nose obstructed; must breathe through mouth. Boring in the nose. Coryza; discharge blood-streaked, watery. Nose completely stopped, with fluent, acrid discharge. Hay-fever. Large scabs high up on right side of nose. Constant picking at nose until it bleeds. Scarlet rash; raw, bloody surfaces anywhere. Impetigo contagiosa. 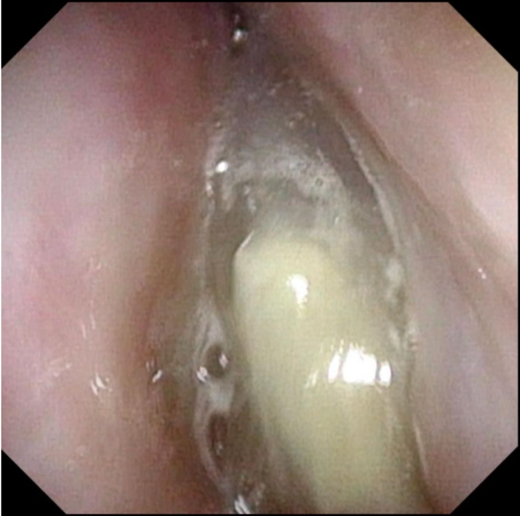
Swelling of sub-maxillary glands. Constricted and swollen; burns; raw. Constant hawking. Hoarseness. Expectoration of much mucus. Lungs feel sore. Clergyman’s sore throat. Voice uncertain, uncontrollable. Worse, talking, singing.
Kali Bichromicum
Acne. Papular eruptions. Ulcer with punched-out edges, with tendency to penetrate and tenacious exudation. Pressure and pain at root of nose and sticking pain in nose. Septum ulcerated, round ulcer. Fetid smell. Discharge thick, ropy, greenish yellow. Tough, elastic plugs from nose; leave a raw surface. Inflammation extends to frontal sinuses, with distress and fullness at root of nose. Polyps. Dropping from posterior nares. Loss of smell. Much hawking. Inability to breathe through nose. Dryness. Coryza, with obstruction of nose. Violent sneezing. Profuse, watery nasal discharge. Chronic inflammation of frontal sinus with stopped-up sensation.
Kali Nitricum
Sneezing. Swollen feeling; worse, right nostril. Point red and itching. Polypus. congestion of lungs. Spasmodic croup; paroxysm of crowing. Laryngeal diphtheria. Tongue red, with burning pimples; burns at tip. Throat constricted and sore.
Teucrim Marum Varum
Nasal and rectal symptoms marked. Polypi. Suitable after too much allopathic medicines have been taken. Over sensitiveness. Desire to stretch. A remedy of first importance in chronic nasal catarrh with atrophy; large, offensive crusts and clinkers. Ozaena. Loss of sense of smell. Catarrhal condition of both anterior and posterior nostrils. Mucous polypus. Chronic catarrh; discharge of large, irregular clinkers. Foul breath. Crawling in nostrils, with lachrymation and sneezing. Coryza, with stoppage of nostrils.
Allium Cappa
Coryza, with acrid nasal discharge and laryngeal symptoms. Sneezing, especially when entering a warm room. Copious, watery and extremely acrid discharge. Feeling of a lump at root of nose. Hay-fever. Fluent coryza with headache, cough, and hoarseness. Polypus. Tickling in larynx.
Alumen
Throat relaxed. Mucous membrane red and swollen. Cough. Tickling in throat. Tendency to throat colds. Enlarged and indurated tonsils. Ulcers, with indurated base. To be thought of in indurated glands, epithelioma. Veins become varicose and bleed. Indurations resulting from long-continued inflammatory irritations. Glands inflame and harden.
Aranea Deadema
Bones affections. Catalepsy. Hydrogenous constitution (sensitive to seasons – allergies/Hay fevers). Polypi, tubercles, warts epithelioma, naevi, carbuncles; ulcers, especially in ano-genital region. Freckles and blotches. Hemoptysis. Dry skin, with brown spots. Zona; herpetic eruptions. Tearing pains in glands. Glandular enlargement. Nails crippled; brittle and soft. Sarcoma; polypi. Brown spots on hands and arms.
Aurum Metallicum
Aurum develops in the organism, by attacking the blood, glands, and bone. Caries of ossicula and of mastoid. Obstinate fetid otorrhea after scarlatina. External meatus bathed in pus. Chronic nerve deafness; Labyrinthine disease due to syphilis.
Nose ulcerated, painful, swollen, obstructed. Inflammation of nose; caries; fetid discharge, purulent, bloody. Boring pains in nose. Putrid smell from nose. Sensitive smell. Horrible odor from nose and mouth. Knobby tip of nose. Dyspnea at night. Frequent, deep breathing. 
Lemna Minor
A catarrhal remedy. Acts especially upon the nostrils. Nasal polypi; swollen turbinate. Atrophic rhinitis. Asthma from nasal obstruction; worse in wet weather. Putrid smell; loss of smell. Crusts and muco-purulent discharge very abundant. Post-nasal dropping. Pain like a string from nostrils to ear. Reduces nasal obstruction when it is an edematous condition. Dryness of naso-pharynx.
Psoronium
Dry, coryza, with stoppage of nose. Chronic catarrh; dropping from posterior nares. Acne rosacea. Herpes from temples over ears to cheeks. Offensive discharge from eczema around ears. Intolerable itching. Chronic otorrhea. Most fetid pus from ears, brownish, offensive. Swelling of upper lip. Pale, delicate. Humid eruption on face. Sickly.
Cadmium Sulphuratum
Ozaena. Tightness at root. Nose obstructed, polypus. Caries of nasal bones. Boils on nose. Nostrils ulcerated. Trembling of jaw. Facial paralysis. Difficult swallowing. Esophagus constricted. Salty belching. Intense nausea.
Calcarea Carbonica
Dry, nostrils sore, ulcerated. Stoppage of nose, also with fetid, yellow discharge. Offensive odor in nose. Polypi; swelling at root of nose. Epistaxis. Coryza. Takes cold at every change of weather. Catarrhal symptoms with hunger; coryza alternates with colic.
Conium Maculatum
Nose bleeds easily-becomes sore. Polypus. Axillary glands pain, with numb feeling down arm. Yellow skin, with papular eruption; yellow fingernails. Glands enlarged and indurated, also mesenteric. Flying stitches through the glands. Tumors, piercing pains. Chronic ulcers with fetid discharge.
Carbo Vagitablis
Senile gangrene. Ichorous, offensive discharge; tendency to gangrene of the margins. Purpura. Varicose ulcers. Epistaxis in daily attacks, with pale face. Bleeding after straining, with pale face; tip of nose red and scabby, itching around nostrils. Varicose veins on nose. Eruption in corner of alae nasi. Coryza with cough, especially in moist, warm weather. Ineffectual efforts to sneeze.
Natrum Sulph
Sycotic excrescences; wart-like red lumps all over body. Dyspnea, during damp weather. Nasal catarrh, with thick, yellow discharge and salty mucus. Coryza. Epistaxis. Ethmoiditis. 
Formica
Tuberculosis, carcinoma, and lupus; chronic nephritis. Complaints from overlifting. Apoplectic diseases. Has a marked deterrent influence on the formation of polypi.
Formicum Acidium
Tuberculosis, chronic nephritis, malignant tumors; pulmonary tuberculosis (not in third stage), lupus; carcinoma of breast and stomach. TB. Lupus. Varicose. Polyps. Pain in aponeurosis and muscles of head, neck and shoulders…) {Dulcamara, Urtica urens and Juniperus also contains formic acid}
Dulcamar
Adenitis. Pruritus, always worse in cold, wet weather. Herpes zoster, pemphigus. Swelling and indurated glands from cold. Vesicular eruptions. Sensitive bleeding ulcers. Little boils. Red spots, urticaria, brought on by exposure, or sour stomach. Humid eruptions on face, genitals, hands, etc. Warts, large, smooth, on face and palmar surface of hands. Anasarca. Thick, brown-yellow crusts, bleeding when scratched. Dry coryza. Complete stoppage of nose. Stuffs up when there is a cold rain. Thick, yellow mucus, bloody crusts. Profuse coryza. Wants nose kept warm, least cold air stops the nose.
Urtica Urens
Lumps and red spots on hands and fever blisters on lips, itching. Heat in skin of face, arms, shoulders, and chest, with formication, numbness and itching, lips, nose, and ears swollen, lids so edematous that they could scarcely be opened, after a while upper part of body as far as navel edematous and pale, transparent blisters filled with serum and looking like sudamina, becoming confluent and making the skin look wrinkled, lids closed, forming transparent, here and there bluish shining swellings: disappeared on sixth day with desquamation.
Outlook / Prognosis
What can I expect if I have nasal polyps?
Homeopathic treatment can help you get rid of nasal polyps and make it easier for patient to breathe through nose for ever.
With allopathic treatment unfortunately, polyps can come back after treatment. Some people need to stay on steroid medications or have repeat surgery to manage them.
People with loss of taste (ageusia) and loss of smell (anosmia) may not see a total improvement of symptoms after allopathic treatment. Ask your healthcare provider to refer to the Homeopath instead.
P. S: This article is only for doctors and students having good knowledge about Homeopathy and allopathy.

For proper consultation and treatment, please visit our clinic.
 Dr. Sayyad Qaisar Ahmed (MD {Ukraine}, DHMS), Abdominal Surgeries, Oncological surgeries, Gastroenterologist, Specialist Homeopathic Medicines.
Dr. Sayyad Qaisar Ahmed (MD {Ukraine}, DHMS), Abdominal Surgeries, Oncological surgeries, Gastroenterologist, Specialist Homeopathic Medicines.
Senior research officer at Dnepropetrovsk state medical academy Ukraine.
Location: Al-Haytham clinic, Umer Farooq Chowk Risalpur Sadder (0923631023, 03119884588), K.P.K, Pakistan.
Find more about Dr Sayed Qaisar Ahmed at:
https://www.youtube.com/Dr Qaisar Ahmed